# vuex 源码解读
# vuex 安装
Vue.use(vuex)
在调用Vue.use(vuex)安装 vuex 时会将 vuex 初始化方法与 beforeCreate 钩子绑定混入到 Vue 钩子函数上
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate: vuexInit })
function vuexInit () {
const options = this.$options
// store injection
if (options.store) {
this.$store = typeof options.store === 'function'
? options.store()
: options.store
} else if (options.parent && options.parent.$store) {
this.$store = options.parent.$store
}
}
在任何 vm beforeCreate 时都会调用 vuexInit,所以在任何组件中都可以通过 this.$store 访问到 store
# new Vuex.store (option) 流程图
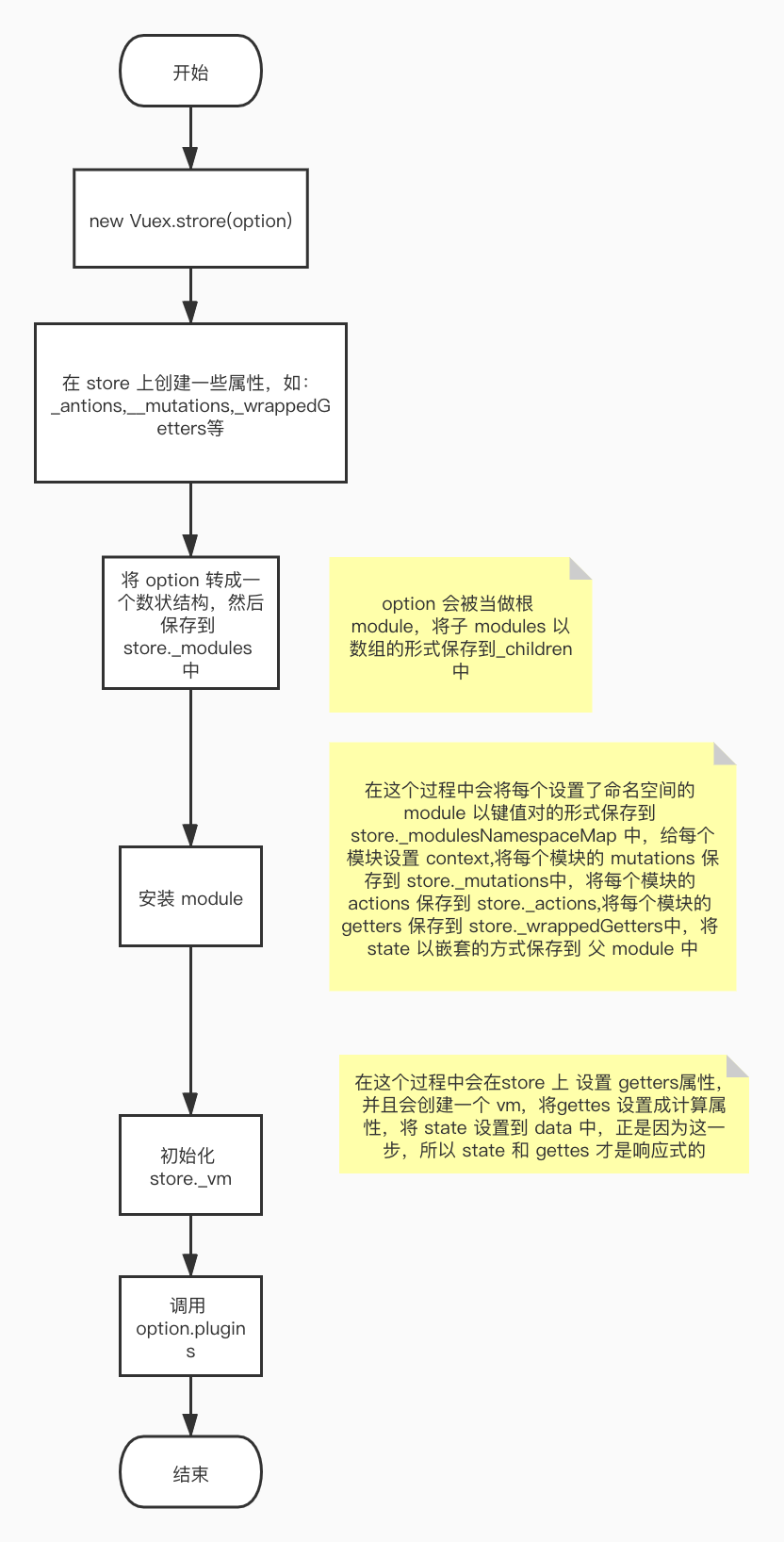
# modules
在 new Vuex.store(option) 时递归 option 中的所有 module,最终生成一个树状结构,new Vuex.store 的参数会被当做 root module
modules 最终会变成如下结构
{
_children:{...},
_rawModule:{...},
state,
...
}
# 安装 modules
安装 modules 时会将根据当前模块是否有命名空间,将这个模块的 mutation,action,getter,state 以模块名加上 type 作为键保存到 store 中的属性中,state 的访问路径与其他的访问路径有所不同
例如:
{
_actions:{
increament:[(...){...}],
a/increament:[(...){...}],
},
_mutations:{
count:[(...){...}],
a/count:[(...){...}],
},
_wrappedGetters:{
total(...){...},
a/total(...){...}
},
state:{
num:xxx,
a:{
num:xxx
}
},
_modulesNamespaceMap:{
a/:module
}
}
当做本模块中调用 commit,dispatch,getters,state 时不用带上一个完整的路径名,只需要有本模块中的 type,这是因为 vuex 会重写每个模块的 commit ,dispatch,getters,state API, 在模块内部调用 commit ,dispatch,getters,state 时会根据当前传入的 type,生成一个完整的路径。
例如:
// 在 a 模块中
{
namespaced:true,
state:{
num:0
},
mutations:{
count(state,num){...}
},
actions:{
increament(context,payload){
// 在这里只需要写本模块的 type
context.commit('count',payload)
}
}
}
# 让 getters 随着 state 的变化而变化
用 new Vue 生成一个 vm,将所有的模块中 getters 作为 vm 的计算属性,通过 Object.defineProperty 给 store.getters 定义访问描述符,如下:
forEachValue(wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
// use computed to leverage its lazy-caching mechanism
// direct inline function use will lead to closure preserving oldVm.
// using partial to return function with only arguments preserved in closure environment.
computed[key] = partial(fn, store)
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key],
enumerable: true // for local getters
})
})
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed
})
当访问 this.$store.getters.xxx 时会执行 get ,get 会返回 store._vm 中的计算属性,而store._vm 中的计算属性是通过 state 计算得到的,所有 this.$store.getters.xxx 的值会随着 state 的变化而变化,也正是因为这一步,所以 state 和 getter 才是响应式的
# store.state
因为 store 中所有的 state 被赋值到 vm 的 data 中,所以在访问 this.$store.state 时访问的是 vm 中 data 中的 state
...
get state(){
return this._vm.$$state
}
...
# store.commit
在调用 store.commit 时,会根据 type 从 store._mutations 中找到这个 type 对应 mutation 包裹方法,然后将 store._committing 设置为 true,然后执行 mutation 包裹方法 ,进而执行 mutation 方法。
const entry = this._mutations[type]
this._withCommit(() => {
// handler 是 mutation 包裹方法
entry.forEach(function commitIterator (handler) {
handler(payload)
})
})
# store.dispatch
在调用 store.dispatch 时,会根据 type 从 store._actions 中找到这个 type 对应 action 包裹方法,然后执行 action 包裹方法,进而执行 action 方法
const entry = this._actions[type]
const result = entry.length > 1
? Promise.all(entry.map(handler => handler(payload)))
: entry[0](payload)
# mapState
在代码中直接访问 store 或者 this.$store 取值 state 会不太优雅,如果要取某个有命名空间的模块中的 state 就更让人难受了。 vuex 提供了 mapState 来解决这个问题,在 mapState 中会根据传入的 namespace, 找到这个 namespace 对应的 module,然后从这个 module 的 context 中去取你需要的 state,每个 module 的 context 是在 new Store 安装 modules 阶段生成的
const mapState = normalizeNamespace((namespace, states) => {
const res = {}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !isValidMap(states)) {
console.error('[vuex] mapState: mapper parameter must be either an Array or an Object')
}
normalizeMap(states).forEach(({ key, val }) => {
res[key] = function mappedState () {
let state = this.$store.state
let getters = this.$store.getters
if (namespace) {
const module = getModuleByNamespace(this.$store, 'mapState', namespace)
if (!module) {
return
}
state = module.context.state
getters = module.context.getters
}
return typeof val === 'function'
? val.call(this, state, getters)
: state[val]
}
// mark vuex getter for devtools
res[key].vuex = true
})
return res
})
normalizeNamespace 和 normalizeMap 都是规范传给 mapState 的参数,getModuleByNamespace 根据 namespace 从 store._modulesNamespaceMap 中找到这个 namespace 对应的 module,然后从这个 module 的 context 中取得 state 和 getters
# mapGetters
const mapGetters = normalizeNamespace((namespace, getters) => {
const res = {}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !isValidMap(getters)) {
console.error('[vuex] mapGetters: mapper parameter must be either an Array or an Object')
}
normalizeMap(getters).forEach(({ key, val }) => {
// The namespace has been mutated by normalizeNamespace
val = namespace + val
res[key] = function mappedGetter () {
if (namespace && !getModuleByNamespace(this.$store, 'mapGetters', namespace)) {
return
}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !(val in this.$store.getters)) {
console.error(`[vuex] unknown getter: ${val}`)
return
}
return this.$store.getters[val]
}
// mark vuex getter for devtools
res[key].vuex = true
})
return res
})
mapGetters 和 mapState 的实现很多地方是相同的,他与 mapState 的不同点是取值方式不同,mapGetters 通过 namespace 和 一系列 getter 名,生成一个完成的 getter 路径,然后从 this.$store.getters 中取值。
# mapMutations
在代码中通过 store.commit 或者 this.$store.commit 修改 state 显得不够优雅,当要修改一个带有命名控件的 state,就更让人难受了,因为需要写一个完整的路径。vuex 提供了 mapMutations 语法糖来解决这个问题,在调用 mapMutations 时,你可以传入命名空间和一系列 mutation type, mapMutations 会根据命名空间找到对应的 module, 然后调用这个 module 的 context 中的 commit
const mapMutations = normalizeNamespace((namespace, mutations) => {
const res = {}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !isValidMap(mutations)) {
console.error('[vuex] mapMutations: mapper parameter must be either an Array or an Object')
}
normalizeMap(mutations).forEach(({ key, val }) => {
res[key] = function mappedMutation (...args) {
// Get the commit method from store
let commit = this.$store.commit
if (namespace) {
const module = getModuleByNamespace(this.$store, 'mapMutations', namespace)
if (!module) {
return
}
commit = module.context.commit
}
return typeof val === 'function'
? val.apply(this, [commit].concat(args))
: commit.apply(this.$store, [val].concat(args))
}
})
return res
})
module.context.commit 是重写了 store.commit
# mapActions
const mapActions = normalizeNamespace((namespace, actions) => {
const res = {}
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !isValidMap(actions)) {
console.error('[vuex] mapActions: mapper parameter must be either an Array or an Object')
}
normalizeMap(actions).forEach(({ key, val }) => {
res[key] = function mappedAction (...args) {
// get dispatch function from store
let dispatch = this.$store.dispatch
if (namespace) {
const module = getModuleByNamespace(this.$store, 'mapActions', namespace)
if (!module) {
return
}
dispatch = module.context.dispatch
}
return typeof val === 'function'
? val.apply(this, [dispatch].concat(args))
: dispatch.apply(this.$store, [val].concat(args))
}
})
return res
})
mapActions 与 mapMutations 类似,只是 mapActions 调用的是 dispatch